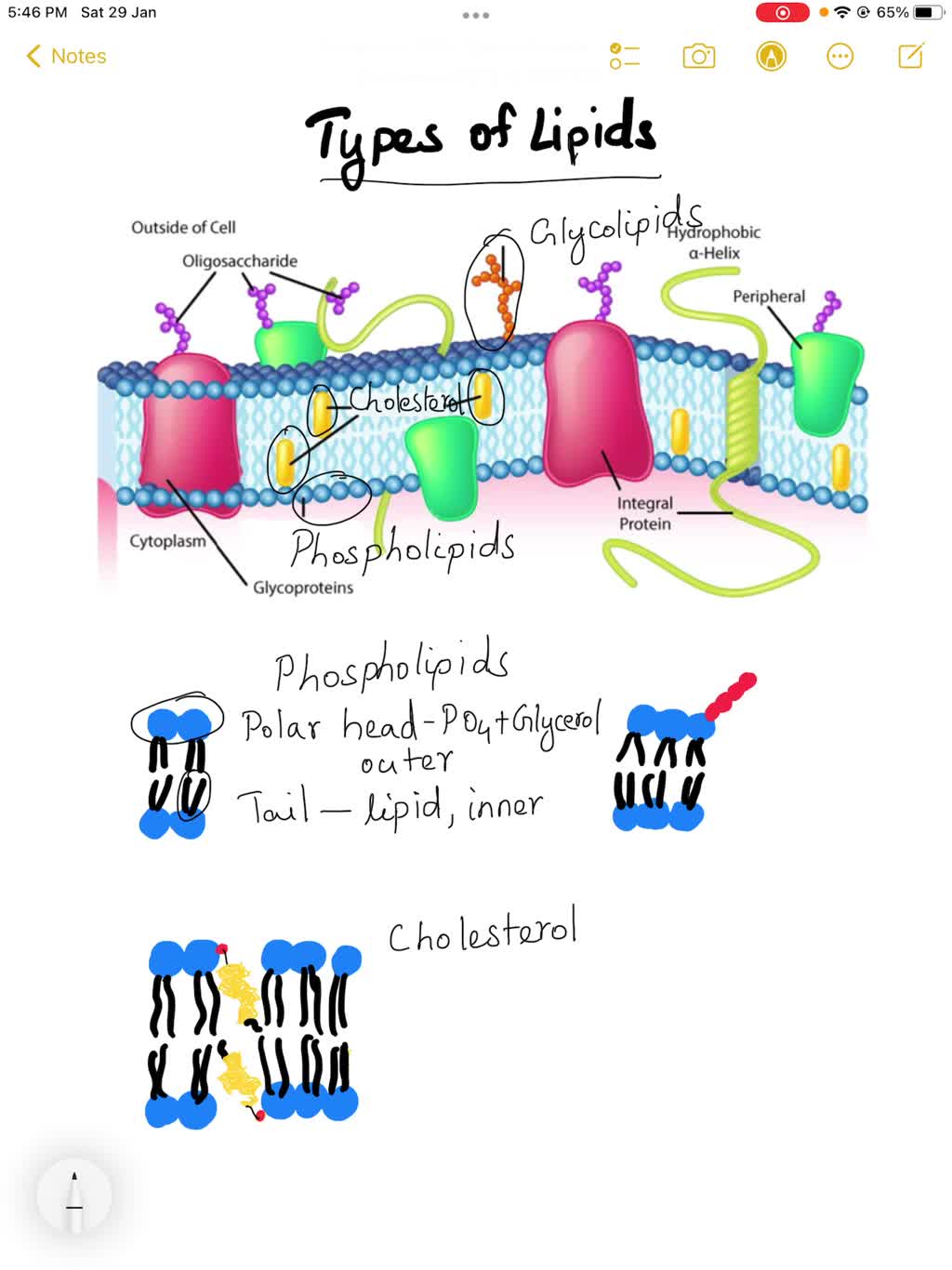
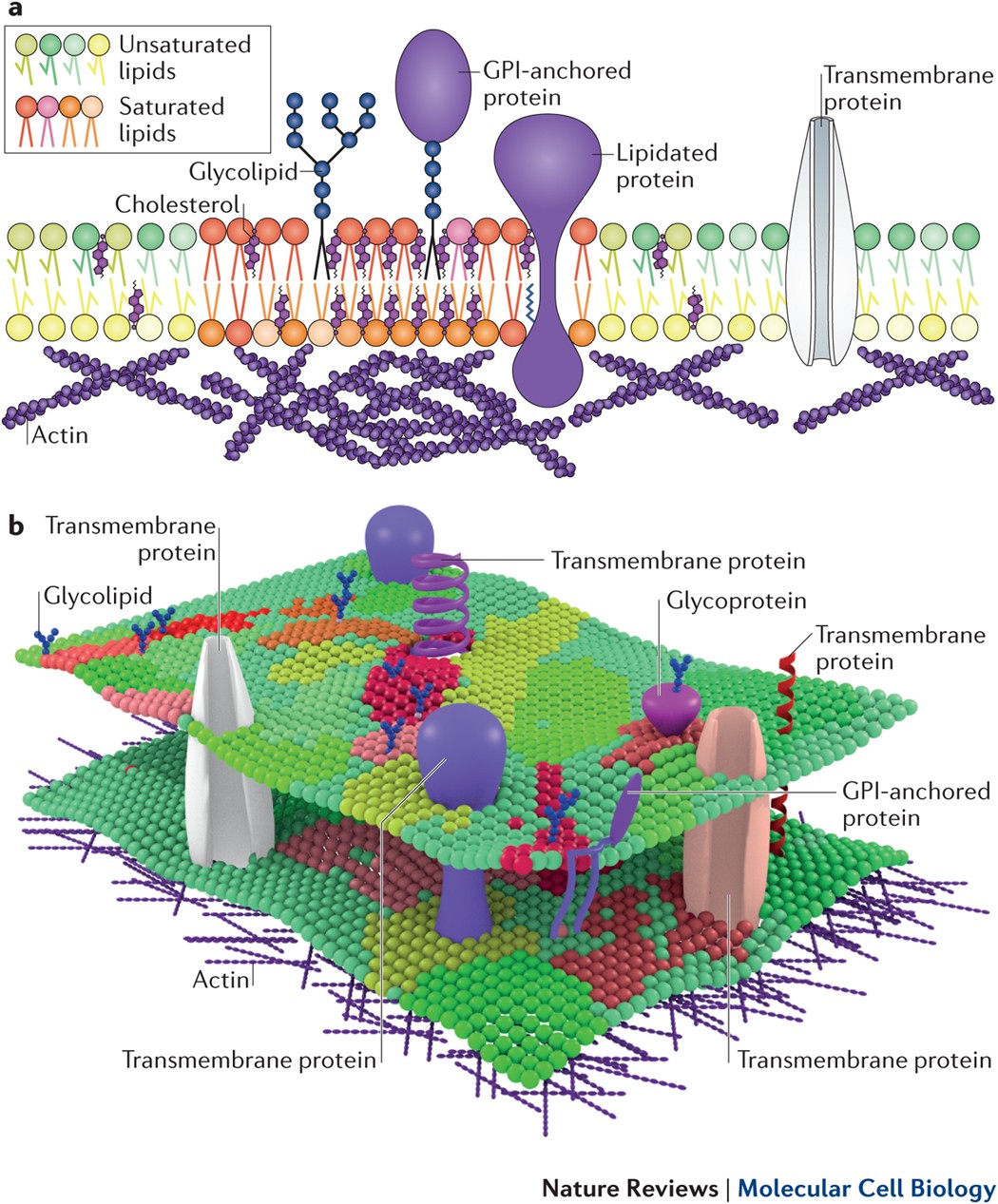
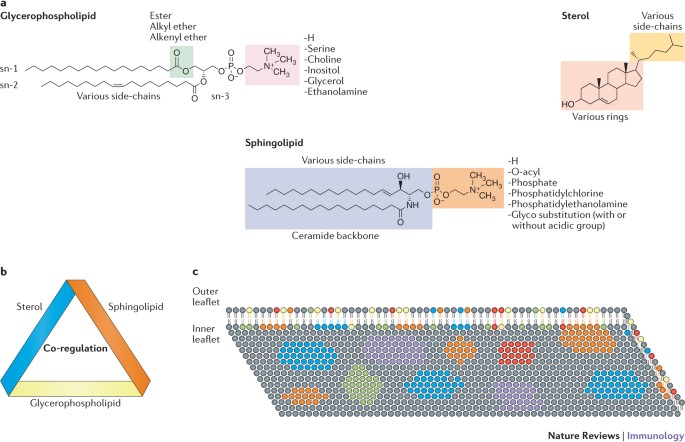
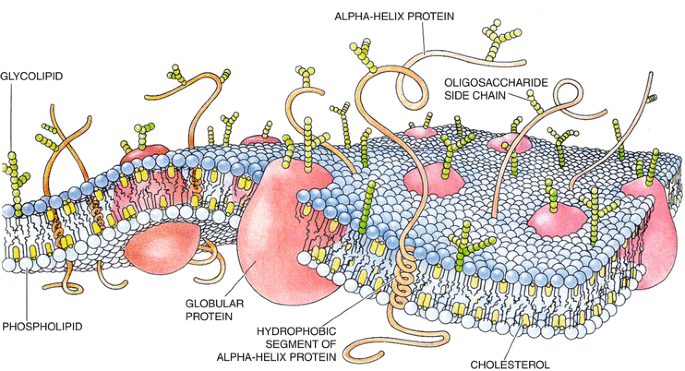
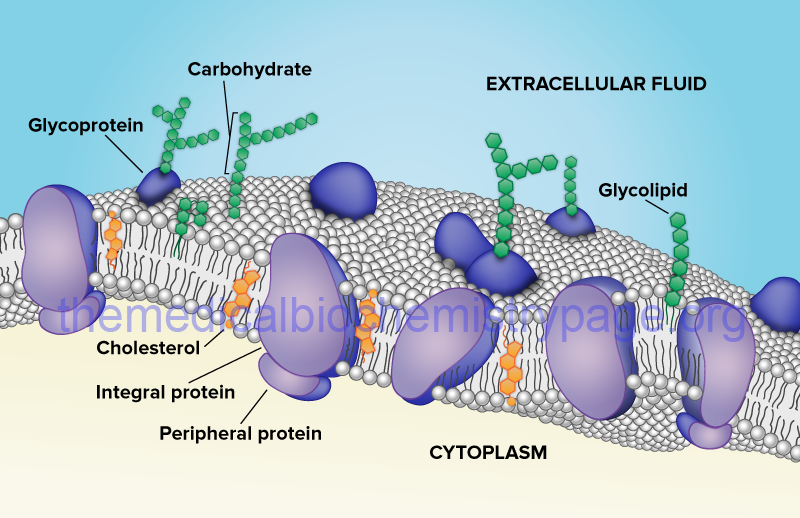
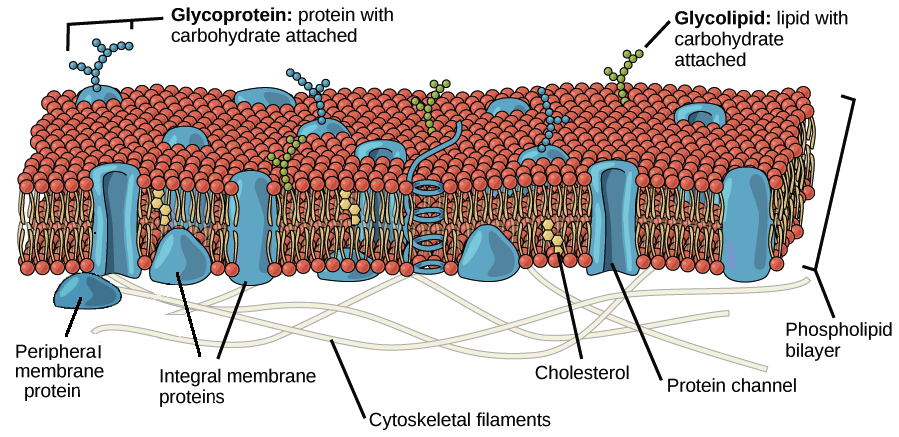
39 label the types of plasma membrane lipids
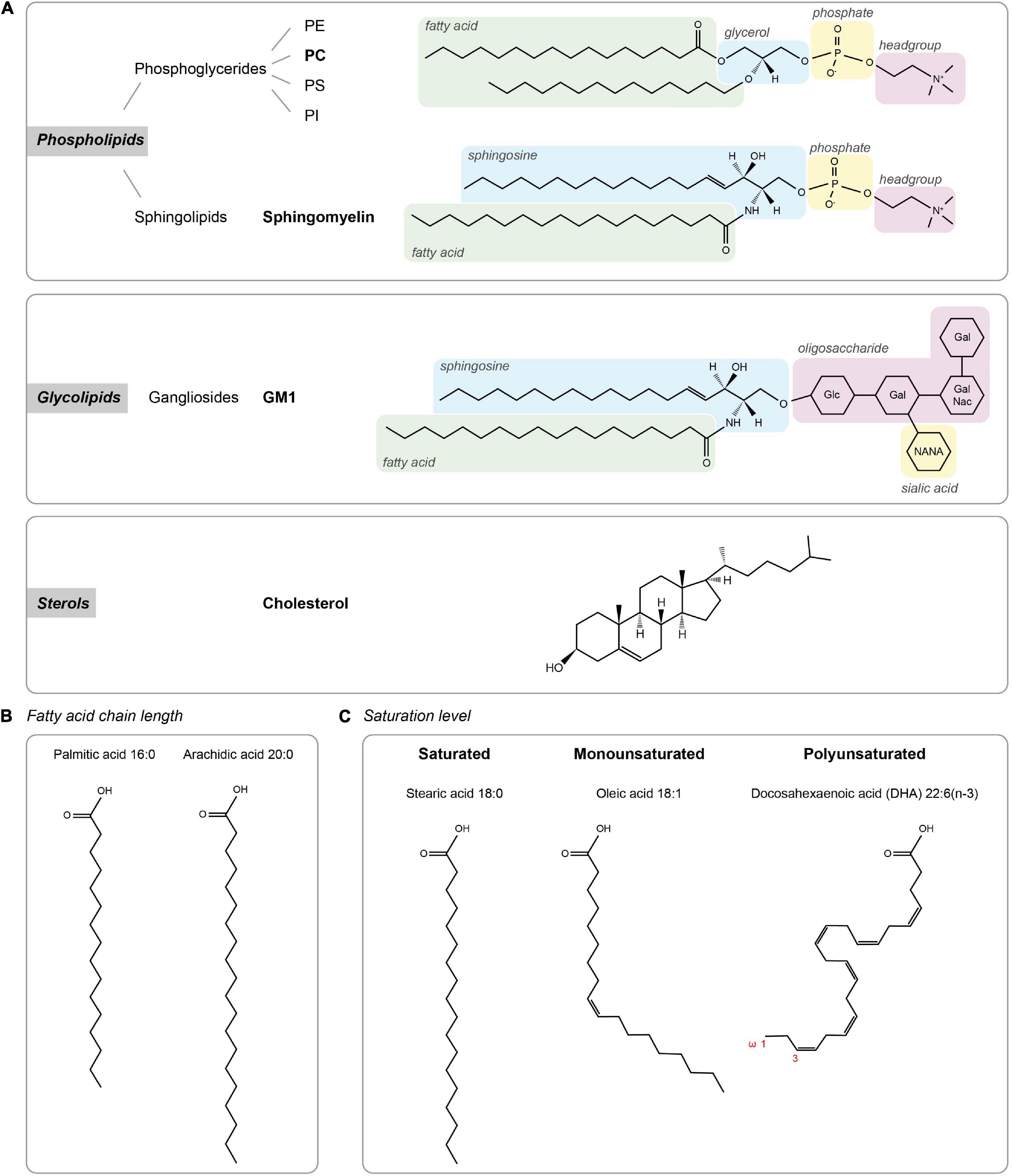
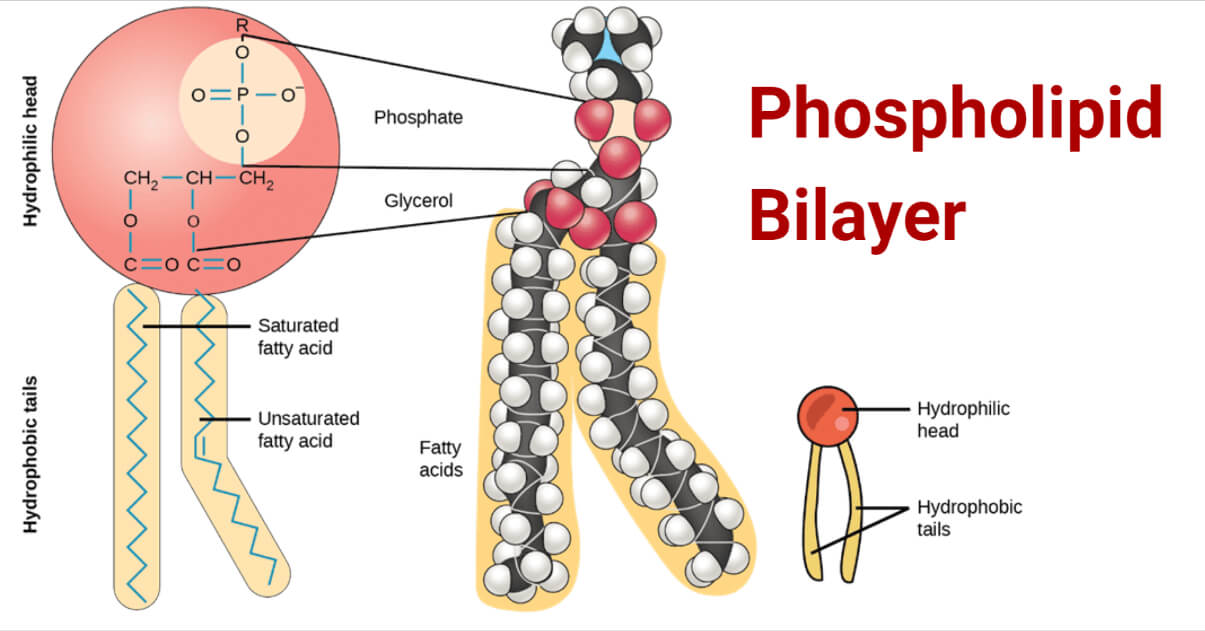
The Lipid Bilayer - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI... Four major phospholipids predominate in the plasma membrane of many mammalian cells: phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylserine, and sphingomyelin. The structures of these molecules are shown in Figure 10-12. Chapter 3 Worksheet Flashcards | Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like determine from the description which cellular structure each phrase is describing. then click and drag each cellular structure into the correct category to indicate whether it is part of the cytoplasm or the cell membrane, click and drag each label into the correct category to indicate whether it pertains to the cytoplasm or the plasma membrane, which membrane-bound organelle is the site of protein and lipid synthesis? and more.
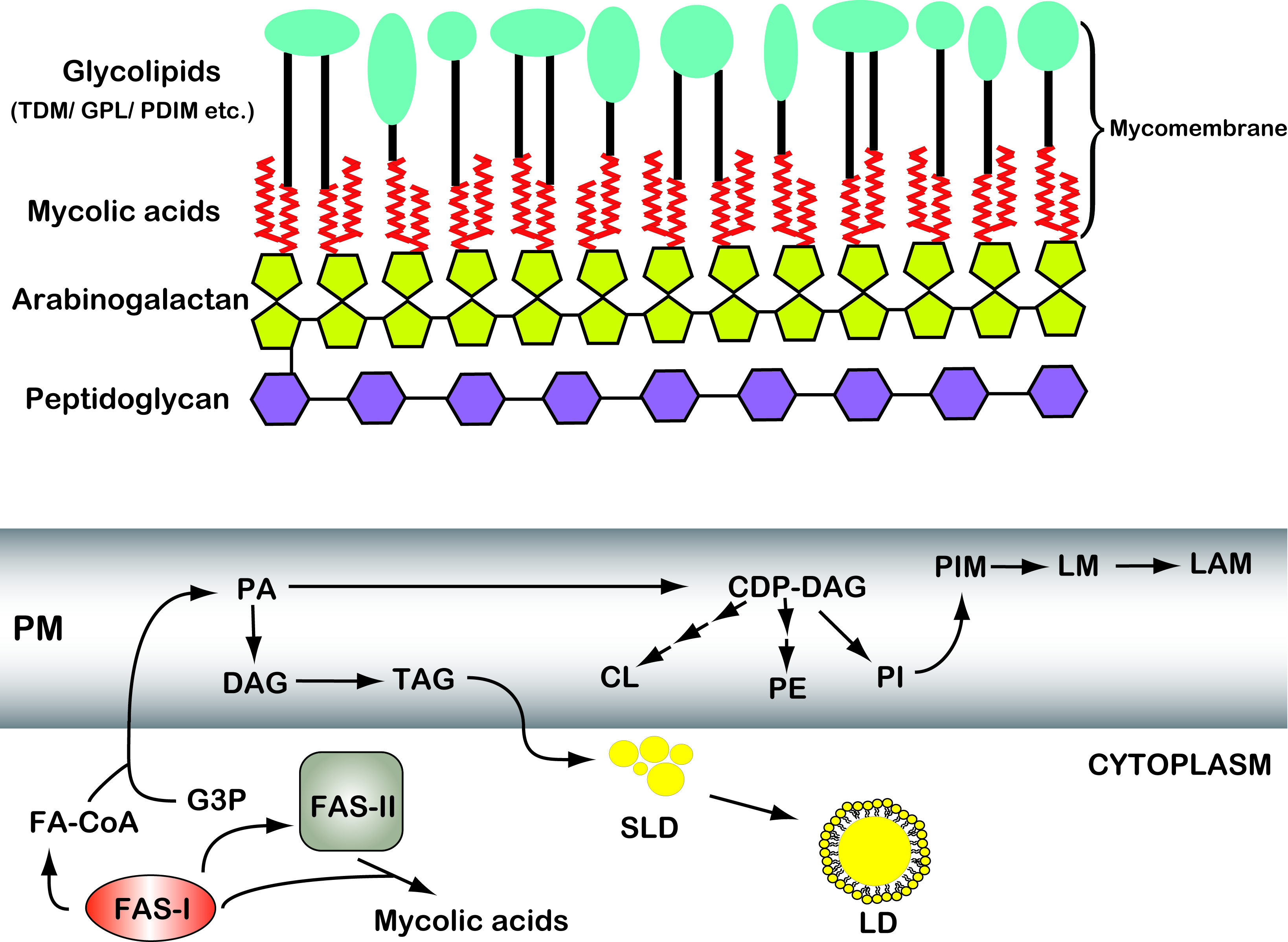
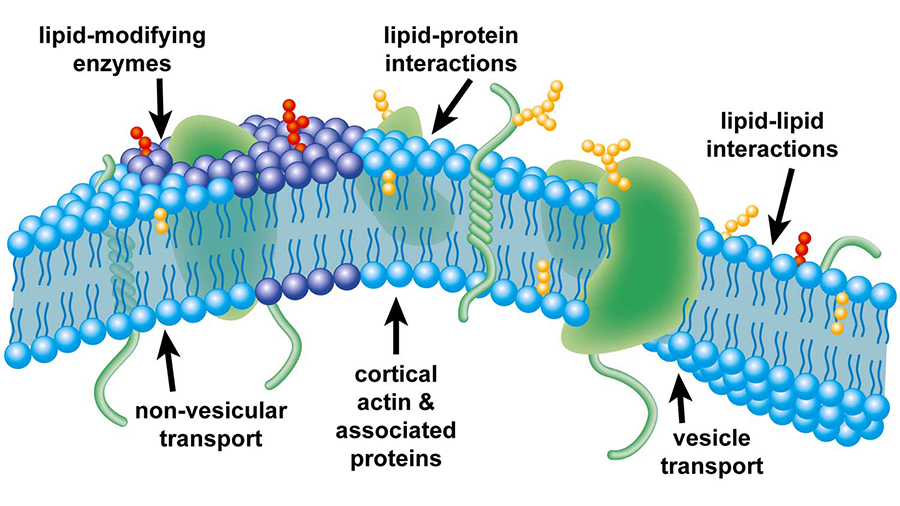
Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane) - Genome.gov Feb 3, 2023 · The plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane, is the membrane found in all cells that separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. In bacterial and plant cells, a cell wall is attached to the plasma membrane on its outside surface. The plasma membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable.

Label the types of plasma membrane lipids
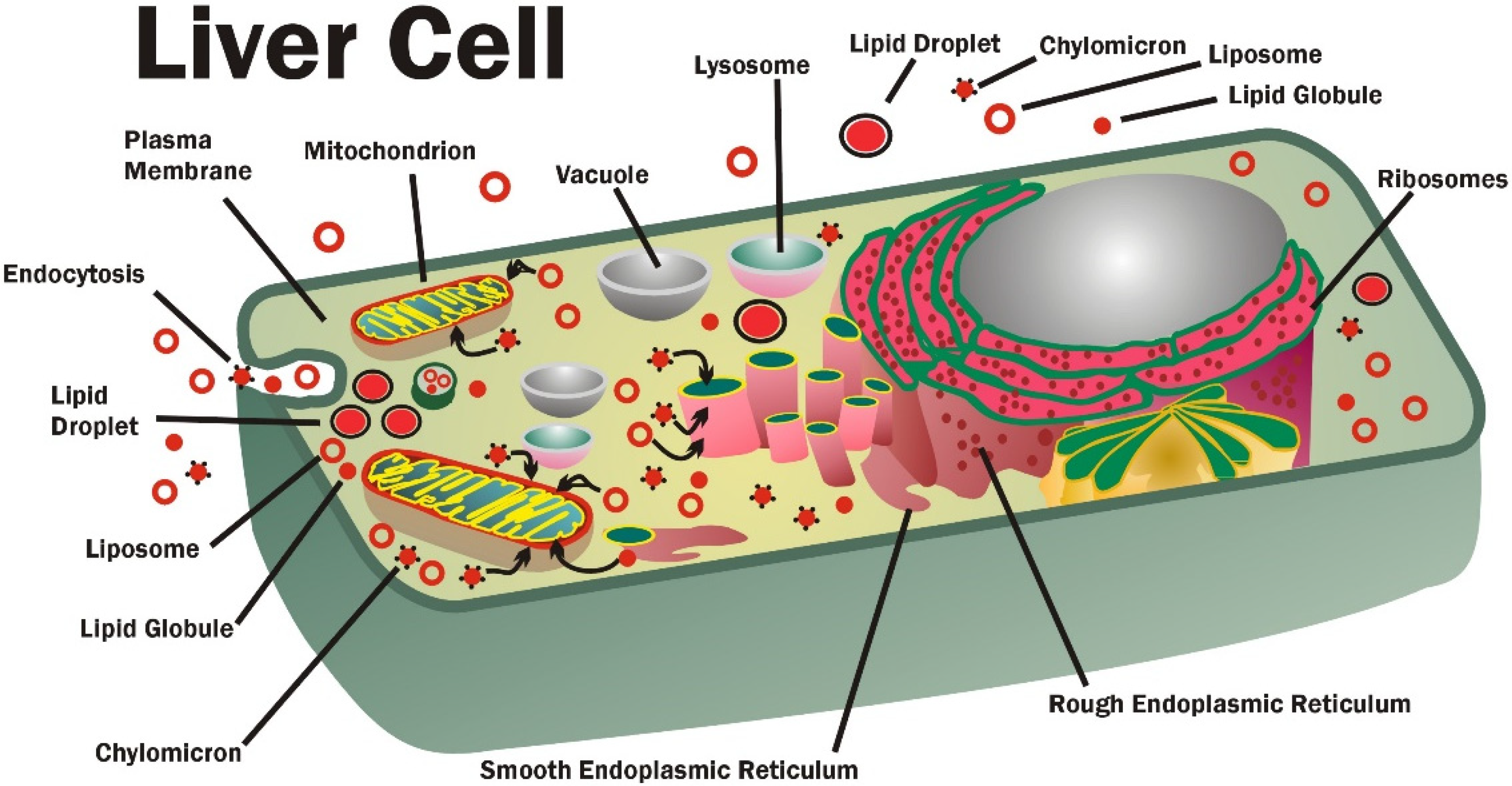
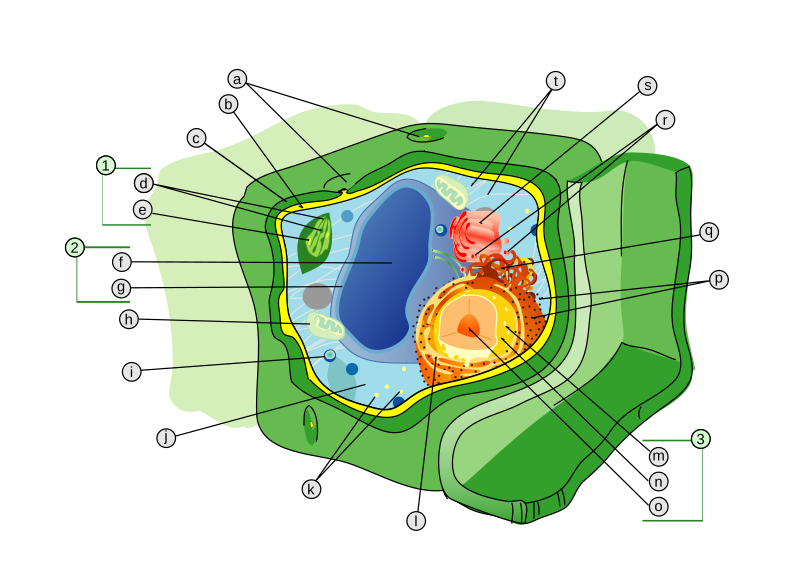
Labeling the Cell Flashcards | Quizlet membrane bound organelles golgi apparatus, mitochondrion, lysosome, peroxisome, rough endoplasmic reticulum nonmembrane bound organelles ribosomes, centrosome, proteasomes cytoskeleton includes microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules Identify the highlighted structures Structures and functions of membrane carbohydrates -glycocalyx Plasma membrane and cytoplasm (article) | Khan Academy The plasma membrane is the border between the interior and exterior of a cell. As such, it controls passage of various molecules—including sugars, amino acids, ions, and water—into and out of the cell. How easily these molecules can cross the membrane depends on their size and polarity. Some small, nonpolar molecules, such as oxygen, can pass directly through the phospholipid portion of the membrane. Plasma Membrane and Lipids Flashcards | Quizlet 7 types of membrane proteins 1. Transporters 2. Enzymes 3. Receptors 4. Signal Transducers 5. Cell Surface Idenity Markers 6. Cell Adhesion Proteins 7. Attachers to the cytoskeleton Can proteins move in the membrane? Yes 2 types of solutes that can diffuse through the cell membrane 1. Noncharged Molecules 2. H20
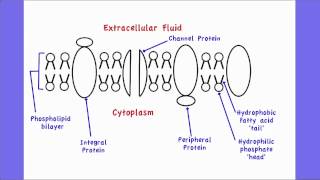
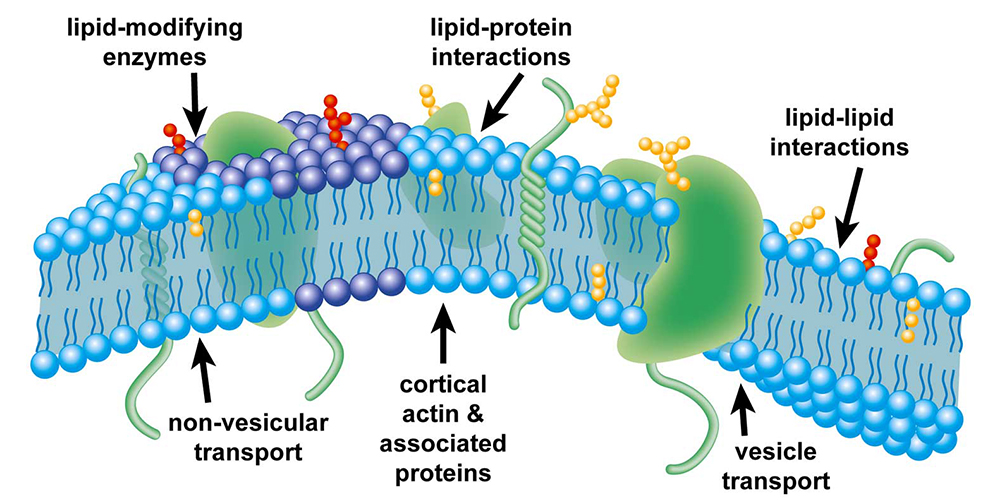
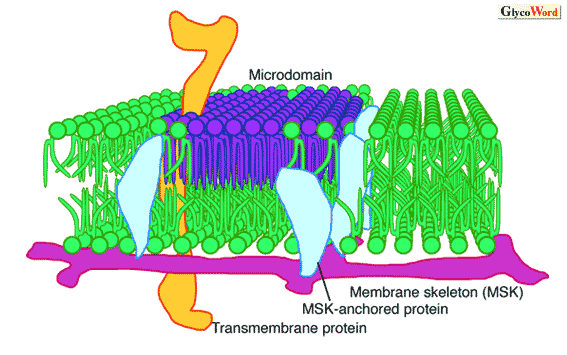
Label the types of plasma membrane lipids. Structure of the Plasma Membrane - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Most plasma membranes consist of approximately 50% lipid and 50% protein by weight, with the carbohydrate portions of glycolipids and glycoproteins constituting 5 to 10% of the membrane mass. Since proteins are much larger than lipids, this percentage corresponds to about one protein molecule per every 50 to 100 molecules of lipid. Plasma Membrane and Lipids Flashcards | Quizlet 7 types of membrane proteins 1. Transporters 2. Enzymes 3. Receptors 4. Signal Transducers 5. Cell Surface Idenity Markers 6. Cell Adhesion Proteins 7. Attachers to the cytoskeleton Can proteins move in the membrane? Yes 2 types of solutes that can diffuse through the cell membrane 1. Noncharged Molecules 2. H20 Plasma membrane and cytoplasm (article) | Khan Academy The plasma membrane is the border between the interior and exterior of a cell. As such, it controls passage of various molecules—including sugars, amino acids, ions, and water—into and out of the cell. How easily these molecules can cross the membrane depends on their size and polarity. Some small, nonpolar molecules, such as oxygen, can pass directly through the phospholipid portion of the membrane. Labeling the Cell Flashcards | Quizlet membrane bound organelles golgi apparatus, mitochondrion, lysosome, peroxisome, rough endoplasmic reticulum nonmembrane bound organelles ribosomes, centrosome, proteasomes cytoskeleton includes microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules Identify the highlighted structures Structures and functions of membrane carbohydrates -glycocalyx

















Komentar
Posting Komentar